Gold has long been revered for its beauty and value, but its utility extends far beyond jewelry and currency. In the modern world, gold plays a crucial role in technology and industry, where its unique properties are harnessed for a variety of applications. This article explores the multifaceted uses of gold in these sectors, highlighting its importance in driving innovation and efficiency.
Properties of Gold That Make It Ideal for Technological Applications
Gold’s unique physical and chemical properties make it an indispensable material in technology and industry. Its excellent conductivity, resistance to corrosion, and malleability are just a few of the characteristics that make it suitable for a wide range of applications.
Conductivity: Gold is an excellent conductor of electricity, which makes it ideal for use in electronic components. Unlike other metals, gold does not tarnish or corrode, ensuring reliable performance over time. This is particularly important in high-precision electronics where even minor degradation can lead to significant performance issues.
Corrosion Resistance: Gold’s resistance to oxidation and corrosion is another reason it is favored in technology. In environments where other metals might degrade, gold remains stable, ensuring the longevity and reliability of components. This property is especially valuable in aerospace and medical applications, where failure is not an option.
Malleability and Ductility: Gold is highly malleable and ductile, meaning it can be drawn into thin wires or hammered into thin sheets without breaking. This allows for the creation of intricate components and connections in electronic devices, where space is often at a premium.
Gold in Electronics
One of the most significant uses of gold in technology is in the electronics industry. Gold is used in a variety of electronic components, including connectors, switches, and relay contacts. Its excellent conductivity and resistance to corrosion make it ideal for these applications.
Connectors and Contacts: Gold is often used to coat connectors and contacts in electronic devices. This ensures a reliable connection and minimizes the risk of signal loss or interference. Gold-plated connectors are commonly found in computers, smartphones, and other consumer electronics.
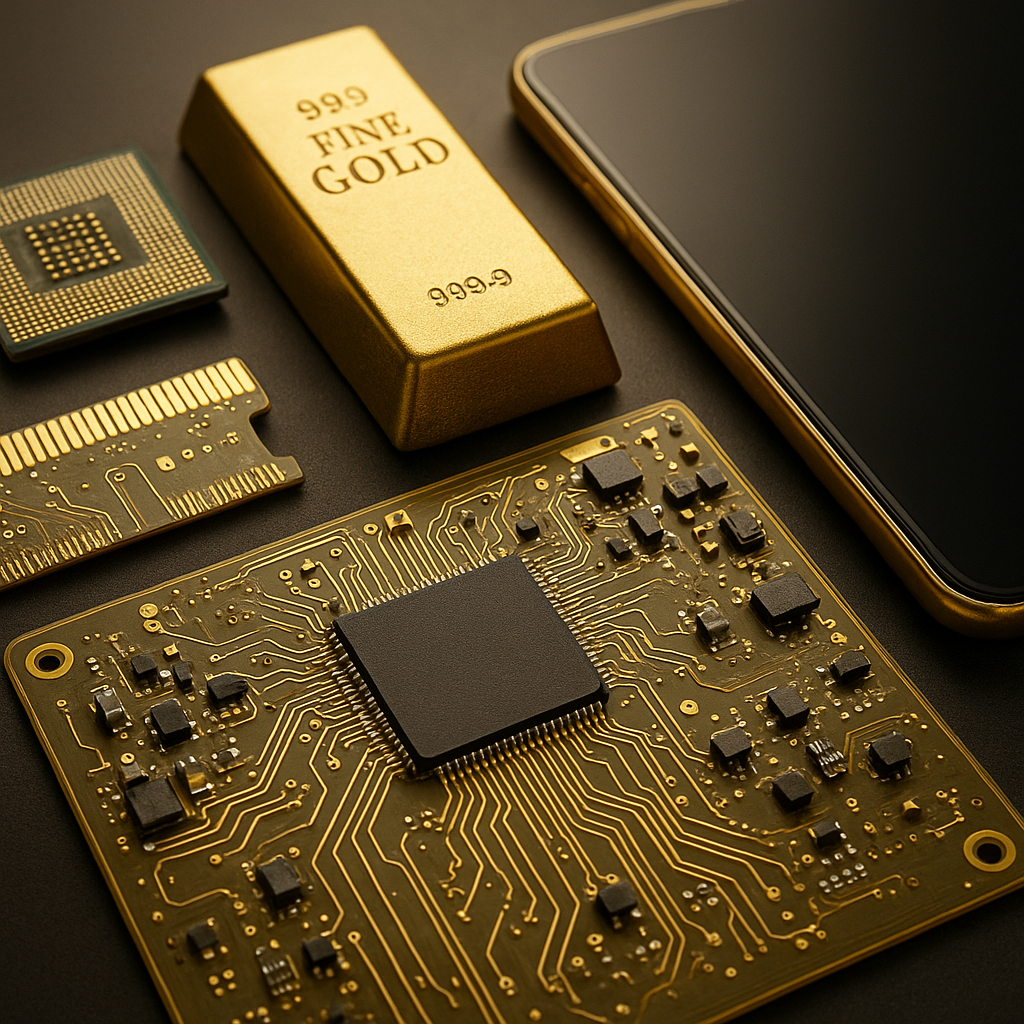
Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs): Gold is used in the production of PCBs, which are the backbone of most electronic devices. The gold is applied to the board’s surface to create a conductive path for electrical signals. This ensures efficient signal transmission and enhances the overall performance of the device.
Semiconductors: Gold is also used in the production of semiconductors, which are essential components of modern electronics. Gold’s stability and conductivity make it an ideal material for creating reliable and efficient semiconductor devices.
Gold in Telecommunications
The telecommunications industry relies heavily on gold for its ability to provide reliable and efficient signal transmission. Gold is used in a variety of components, including connectors, switches, and relay contacts, to ensure the integrity of communication networks.
Fiber Optic Technology: Gold is used in the production of fiber optic cables, which are essential for high-speed internet and telecommunications. The gold coating on the cables helps to enhance signal transmission and reduce signal loss, ensuring fast and reliable communication.
Satellite Technology: Gold is also used in satellite technology, where its resistance to corrosion and excellent conductivity are crucial. Gold-coated components are used in satellites to ensure reliable communication and data transmission, even in the harsh conditions of space.
Gold in Aerospace and Defense
In the aerospace and defense industries, gold is used for its reliability and performance in extreme conditions. Its resistance to corrosion and excellent conductivity make it an ideal material for a variety of applications.
Aerospace Components: Gold is used in the production of aerospace components, including connectors, switches, and relay contacts. Its resistance to corrosion and excellent conductivity ensure reliable performance in the harsh conditions of space.
Defense Technology: Gold is also used in defense technology, where its reliability and performance are crucial. Gold-coated components are used in a variety of defense applications, including radar systems and communication devices, to ensure reliable performance in critical situations.
Gold in Medical Technology
Gold’s biocompatibility and resistance to corrosion make it an ideal material for use in medical technology. It is used in a variety of applications, from diagnostic equipment to implants and prosthetics.
Medical Implants: Gold is used in the production of medical implants, including pacemakers and stents. Its biocompatibility ensures that it does not react with the body, reducing the risk of complications and ensuring the longevity of the implant.
Diagnostic Equipment: Gold is also used in diagnostic equipment, including imaging devices and test kits. Its excellent conductivity and resistance to corrosion ensure reliable performance and accurate results.
Drug Delivery Systems: Gold nanoparticles are used in drug delivery systems to enhance the effectiveness of treatments. The nanoparticles can be engineered to target specific cells or tissues, improving the precision and efficacy of the treatment.
Gold in Renewable Energy
Gold is playing an increasingly important role in the development of renewable energy technologies. Its unique properties make it an ideal material for use in solar cells and fuel cells.
Solar Cells: Gold is used in the production of solar cells, where its excellent conductivity and resistance to corrosion enhance the efficiency of energy conversion. Gold-coated components are used to improve the performance and longevity of solar panels.
Fuel Cells: Gold is also used in fuel cells, where its stability and conductivity are crucial for efficient energy conversion. Gold-coated components are used to enhance the performance and durability of fuel cells, making them a more viable option for renewable energy.
Conclusion
Gold’s unique properties make it an invaluable material in technology and industry. From electronics and telecommunications to aerospace and medical technology, gold plays a crucial role in driving innovation and efficiency. As technology continues to advance, the demand for gold in these sectors is likely to grow, highlighting its importance in shaping the future of industry and technology.